v-innovate Technologies can provide a high-throughput substance detection and analysis technology based on GC-MS/MS, which can be used to analyze the content of terpenoids, metabolic functional characteristics and mechanism of action. The operation process of this method is simplified and easy to implement, and rapid and highly selective analysis reports can be obtained to help researchers explore the role of terpenoids in plant growth and their development and application in food safety and quality.
Terpenoids are a general term for a class of compounds with different numbers of isoprene units as the backbone. Terpenoids produce a variety of endogenous hormones and protect plants from the damage of strong light. The signal substances and allelochemicals in terpenoids play a key role in the plant defense system. Terpenoids have biological activities such as anti-inflammatory, anti-tumor and antibacterial activities. They are the effective ingredients of drugs and are widely used in the health care industry and the medical industry. Monoterpenes and sesquiterpenes often exist in higher plants in the form of volatile oils. Diterpenoids are commonly found in plants in the form of resins. Among them, diterpenoid gibberellin is a plant hormone that can regulate the height of plant growth. Triterpene compounds mainly include triterpene saponins, cucurbitacin, and limonoid. Tetraterpenoids mainly include lutein, lycopene, carotene, etc. Among them, carotene can be transformed into plant hormones such as abscisic acid and cytokinin. MS-based high-throughput substance detection and analysis technology MS instrument can be used in conjunction with gas chromatography (GC), which can effectively identify and determine the content of terpenoid medicinal plants to obtain a comprehensive functional analysis and disclosure of the biological activity of terpenoids Metabolic active molecules and mechanisms of terpenoids.
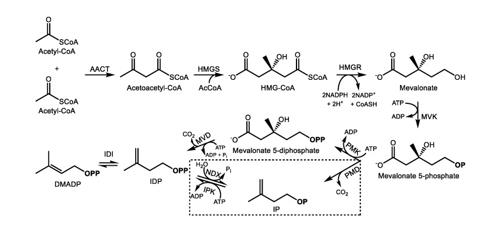 Figure 1. Biosynthesis of isopentenyl (IDP) and dimethylallyl diphosphate (DMADP) via the mevalonic acid (MVA) pathway and alternative MVA pathway (boxed) in the cytosol. (Bergman 2019).
Figure 1. Biosynthesis of isopentenyl (IDP) and dimethylallyl diphosphate (DMADP) via the mevalonic acid (MVA) pathway and alternative MVA pathway (boxed) in the cytosol. (Bergman 2019).
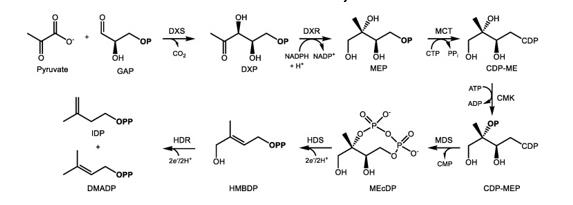 Figure 2. Biosynthesis of IDP and DMADP via the MEP pathway in the plastid. (Bergman 2019).
Figure 2. Biosynthesis of IDP and DMADP via the MEP pathway in the plastid. (Bergman 2019).
In our operating technical process, sample processing does not require derivatization. After the sample is purified, the sample can be directly analyzed, which simplifies the operation process and shortens the analysis time. At the same time, the automatic sampling mode can greatly reduce human errors and ensure the results. Scientific accuracy.
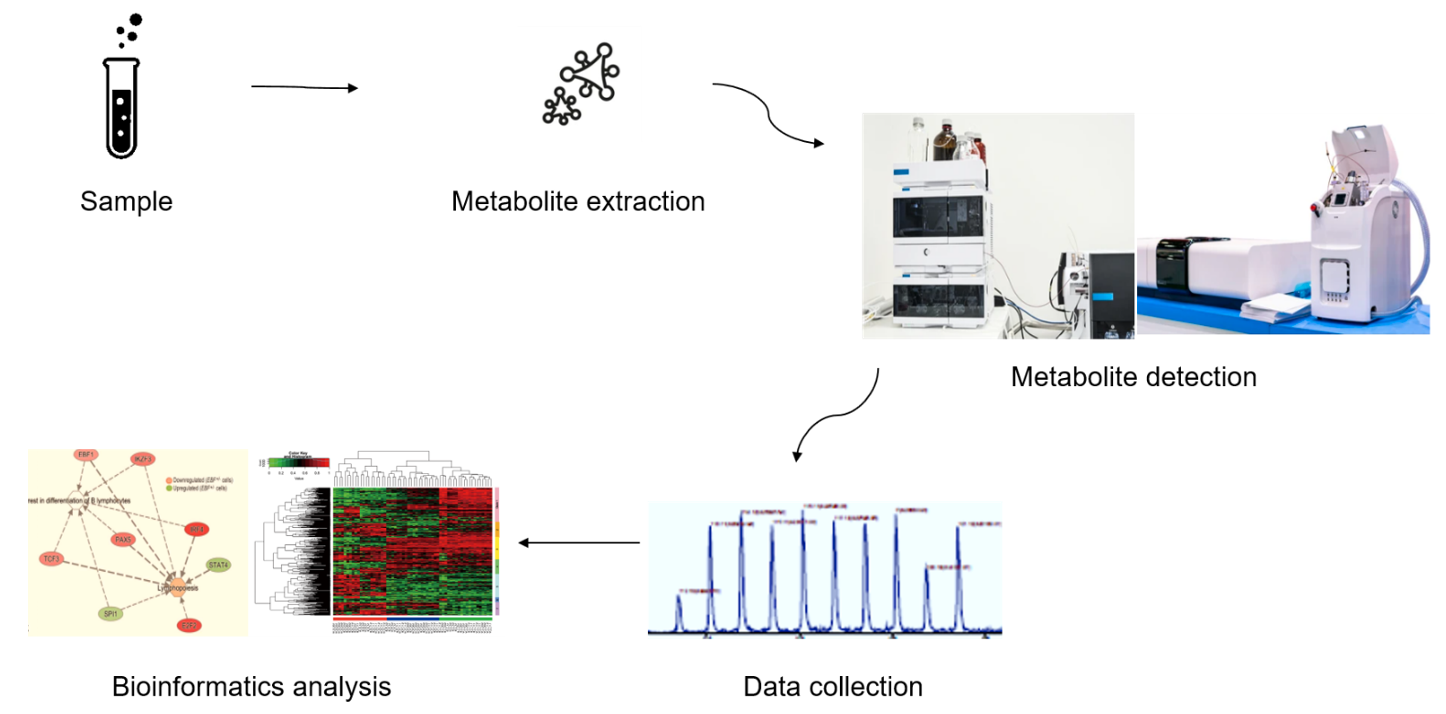 Figure 3. Terpenoids analysis service workflow.
Figure 3. Terpenoids analysis service workflow.
Detection method: external standard method or isotope-labeled internal standard method
Carrier gas: high purity helium
Flow rate: 1 ml/min
Retention reaction time: 1 min
Injection volume: 1 ul
Analysis content:
1. Tissues such as leaves, roots, stems, flowers, fruit pulp, peel tissue, etc., larger leaves need to be quickly cut into pieces with scissors, and the separated samples are quickly washed with sterilized water, and the absorbent paper is immediately put into the liquid after absorbing the excess water. Quickly freeze in nitrogen for more than 2 minutes, and then transfer to -80°C for storage to avoid repeated freezing and thawing.
2. For each sample, take no less than 3 g for fresh samples, no less than 1 g for dry samples. At least three biological replicates in each group, prepare a backup. The measured sample will not be returned, please keep a backup.
※The project items are constantly being updated, not only those listed, please contact our staff via email to get more latest information and related information.
The method based on the combined use of GC and MS can effectively identify, detect and determine the content of terpenoids and their metabolites, and can provide customers with high-quality and comprehensive terpenoid functional activity analysis and molecular mechanism research analysis reports. v-innovate Technologies is dedicated to providing you with a screening strategy for optimizing lead compounds of plant terpenoids and new methods to clarify the complex biochemical pathways of existing candidate compounds.
References
