v-innovate Technologies' targeted metabolomics services target specific metabolites and pathways of interest, which can accurately monitor dynamic metabolic processes, reveal related metabolic mechanisms and verify potential metabolic biomarkers, to guide your research with reliable and accurate measurement results.
Nicotinamide adenine dinucleotide phosphate (NADPH) is reduced coenzyme II, and its scientific name is reduced nicotinamide adenine dinucleotide phosphate, which is a coenzyme.
It plays a role as a hydrogen transporter in many chemical reactions in organisms, which is of great significance. It participates in a variety of anabolic reactions, such as the synthesis of lipids, fatty acids and nucleotides, and can also provide energy for the fixation of carbon dioxide in the dark reaction. These reactions require NADPH as a reducing agent and a donor of hydride ions, and NADPH is the reduced form of NADP+.
Its chemical formula is C21H29N7O17P3, and CAS number is 53-59-8.
MS-based technical means can realize the qualitative and quantitative analysis of nicotinamide adenine dinucleotide phosphate.
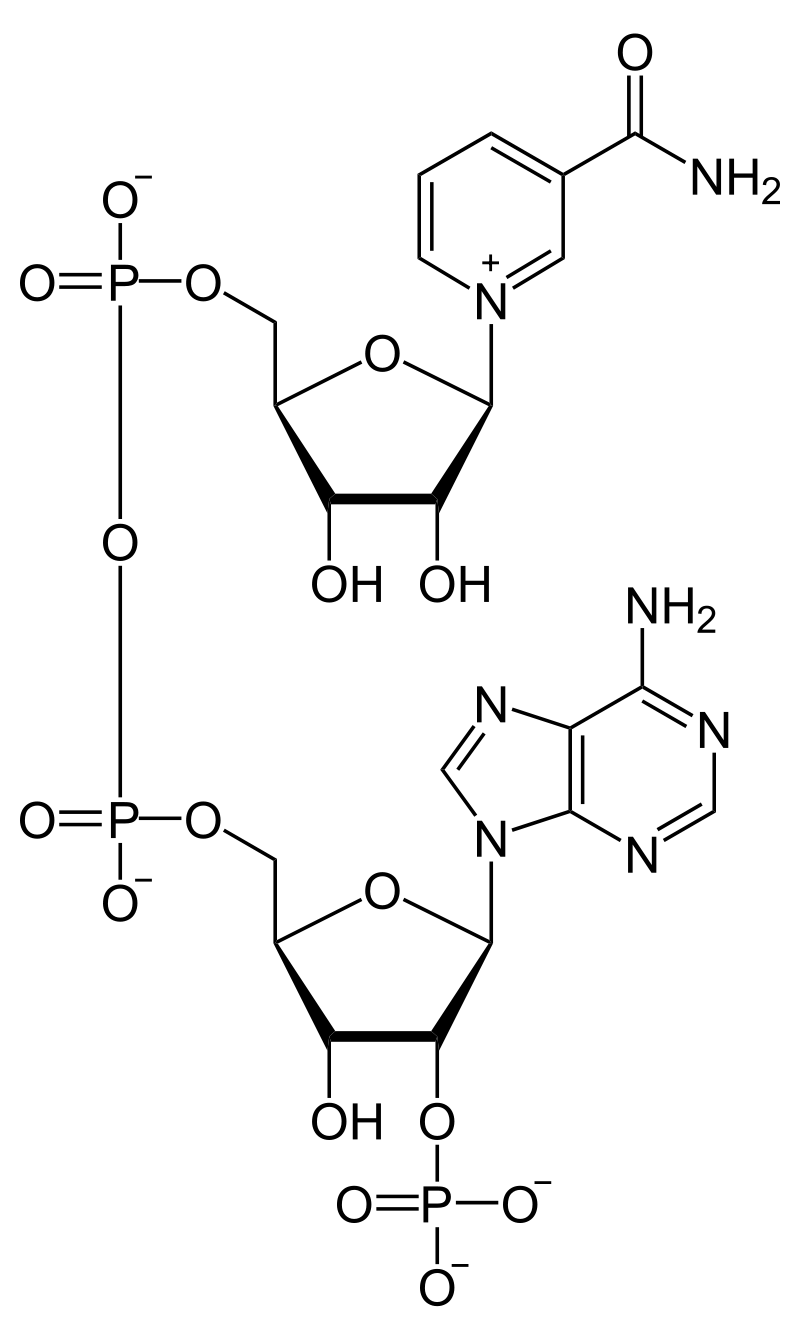 Molecular structure of nicotinamide adenine dinucleotide phosphate
Molecular structure of nicotinamide adenine dinucleotide phosphate
| Sample type |
| Plants, yeasts, microorganisms, etc. Serum, plasma, urine, bile, bile acid, etc. Cells, liver, brain tissue and other animal tissues and feces, etc. There is no restriction on plant varieties. For varieties with special requirements or rare varieties, please contact our staff for more information. |
| Sample demand |
| Plant root / stem / leaf / fruit / seed > 200 mg fresh weight, freeze-dried sample > 0.5 g Cells / microorganisms / cell supernatant / culture medium supernatant: the number of cells or bacteria > 107, supernatant > 2 ml Serum / plasma / urine / ruminal fluid / cerebrospinal fluid / amniotic fluid and other homogeneous liquid samples > 200 µl. (Hemolysis should be avoided. Cerebrospinal fluid can be as low as 100 µl.) Animal tissue / feces related samples > 200 mg / sample For other sample types, please consult technical support or sales. |
| Sample mixed and repeat |
| In order to ensure the accuracy of the samples and reduce systematic errors during sampling, it is necessary to select more than 3 materials with the same condition for each sample. ※ The same condition refers to the same period, basically the same phenotype, and the same part. It is recommended that prepare more than 6 biological replicates. |
| Storage and transportation |
| Quick-frozen preservation with liquid nitrogen can minimize the leakage time of plant samples at room temperature, and store it at -80°C. Dry ice transportation (about 3~4 kg dry ice is consumed every day, please use sufficient dry ice for transportation). |
v-innovate Technologies will provide you with detailed technical reports, including
v-innovate Technologies offers several approaches to metabolomics studies, delivers precise and detailed data and analysis report. We can also customize the methods or establish new methods together with our collaborators, so they are fit-for-purpose and meet your specific needs. If you have any questions or specific requirements, please feel free to contact us.
References
