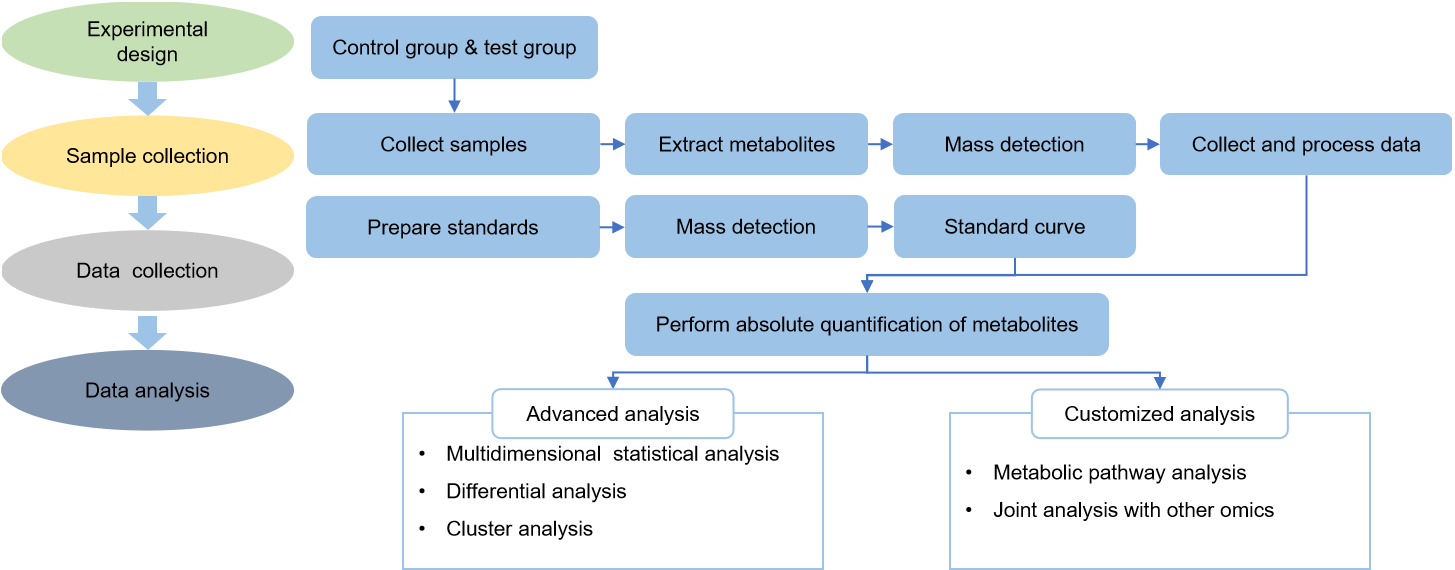
v-innovate Technologies' targeted metabolomics services target specific metabolites and pathways of interest, which can accurately monitor dynamic metabolic processes, reveal related metabolic mechanisms and verify potential metabolic biomarkers, to guide your research with reliable and accurate measurement results.
About Malic Acid
Malic acid (malate, 2-hydroxybutanedioic acid) is a tetracarbon dicarboxylic acid. In nature, malic acid exists in three forms, D-malic acid, L-malic acid and DL-malic acid. Malic acid in nature is the L-form, which is found in almost all fruits, most of all in drupe fruits.
L-malic acid is an important organic acid produced during the metabolism of living organisms and has many biological functions and biological activities, especially in energy metabolism which plays an important role in the protection of human health.
Malic acid is involved in many cellular metabolisms and also acts as a carbon and reducing power carrier in the transfer of carbon and reducing power between cytoplasm and organelles and between organelles.
In mitochondria, malate is an intermediate product of the tricarboxylic acid (TCA) cycle. In C4 plants, malic acid acts as a carrier of CO2 to transport carbon from the chloroplast to the vascular sheath cells, thus achieving synergy between two different cell types in photosynthetic carbon assimilation. In CAM plants, malic acid is stored in the vesicles at night and acts as a CO2 carrier. Malic acid is also involved in the regulation of stomatal opening and closing. In plant cells, malic acid is the substance that links multiple metabolisms of different organelles and is involved in the regulation of multiple metabolic reactions. Malic acid is also widely used in the food and pharmaceutical industries.
v-innovate Technologies provides qualitative and quantitative analysis of malic acid based on HPLC-MS technology to accelerate your project progress.
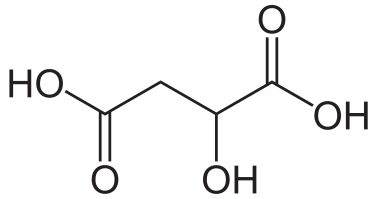 Molecular structure of malic acid
Molecular structure of malic acid
References
