v-innovate Technologies, as a leading biotechnology company, offers reliable, fast and cost-effective glyoxylate and dicarboxylate metabolism analysis service in animal. We use our ample experience, professional expertise, and advanced technologies to speed up your scientific purposes of glyoxylate and dicarboxylate metabolism analysis in animal.
Glyoxylate and dicarboxylate metabolism includes a lot of reactions involving glyoxylate or dicarboxylates. Glyoxylate is the conjugate base of glyoxylic acid, and within a buffered environment of known pH such as the cell cytoplasm. These terms can be used almost interchangeably, as the gain or loss of a hydrogen ion is all that distinguishes them. Similarly, dicarboxylates are the conjugate bases of dicarboxylic acids, a general class of organic compounds containing two carboxylic acid groups like oxalic acid or succinic acid. Glyoxylate and dicarboxylate metabolism is closely related to the Krebs Cycle. When acetyl-coenzyme-A enters the system, it will interact with enzymes within the environment. As one of important carbohydrate metabolisms, glyoxylate and dicarboxylate metabolism play important roles in various diseases like primary hyperoxaluria and Infantile cerebellar-retinal degeneration. As a pioneer in carbohydrate metabolism, v-innovate Technologies provides reliable, rapid and cost-effective glyoxylate and dicarboxylate metabolism analysis service to speed up diseases diagnosis and gain new insights in disease mechanism or treatment.
v-innovate Technologies provides glyoxylate and dicarboxylate metabolism service in a reliable and effective manner, based on our cutting-edge high-performance liquid chromatography (HPLC) platforms. The experimental procedures contain four major steps: sample collection, metabolites extraction, HPLC data analysis and bioinformatics analysis (Figure 1). Our service will be tailored to specific samples and needs for optimal results.
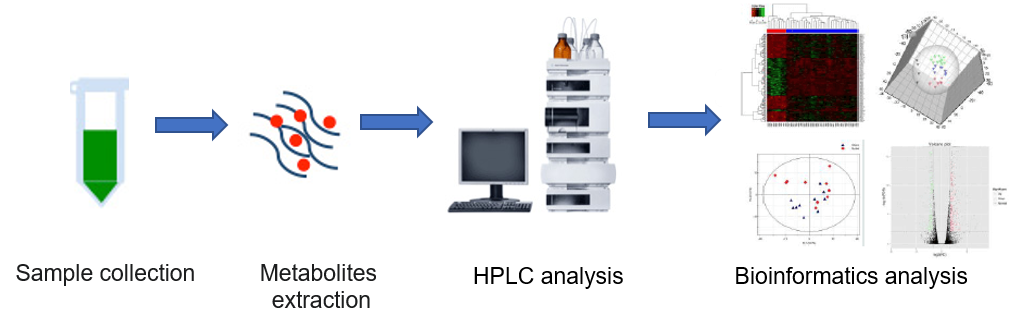 Figure 1. The overall workflow of glyoxylate and dicarboxylate metabolism service.
Figure 1. The overall workflow of glyoxylate and dicarboxylate metabolism service.
| Oxaloacetate | Oxalate | Malate |
| Malonate | Malate | Isocitrate |
| Citrate | Fumarate |
We can analyze a wide range of biological materials including but not limited to cells and solid tissues from humans and animals, such as mice, rats, rabbits. If you need transport your samples to us, please follow the below requirements for different kinds of sample:
Based on advanced HPLC platforms for the determination of glyoxylate and dicarboxylate metabolism, professional bioinformatic analysis software and experienced technicians and scientists, v-innovate Technologies provides customer-tailored glyoxylate and dicarboxylate metabolism analysis service with rapid experimental procedures and easy to read report, to accelerate your scientific research.
References
